Need to check server response codes, redirects, or redirect chains in bulk? Our Status code checker returns the HTTP status code for a whole list of URLs.
This can be useful for finding broken links, checking that all of the URLs in your sitemap are working, and many other things.
HTTP status codes
Before we dive into a practical guide, let’s have a look at basic status codes that can occur and a brief explanation of why you should know about them:
- 200 = OK. This is your ideal status code for your web pages. Everything is working fine and your content isn’t returning any errors.
- 301 = Permanent redirect. A 301 redirect should be used whenever one URL needs to be permanently redirected to another. If you don’t plan to restore page A and want your visitors to go to page B instead, you should use this type of redirect. From an SEO point of view, redirecting pages with this status code is the right thing to do.
- 302 = Temporary redirect. Page A is temporarily redirected to page B. You should use this redirect if you are planning to restore page A, but you don’t want your visitors to visit it for the time being. From an SEO point of view, it is not recommended to redirect pages with this status code (with the exception of the case we have just described above).
- 404 = Not found. The page was not found. If the URL doesn’t exist on the web, we recommend redirecting these pages to the relevant page using the status code 301.
- 410 = Gone. This status code is very similar to the 404 status code, but it is a bit more “permanent”. However, from an SEO point of view, these are very similar situations. Our recommendation is to find internal links that point to 410 pages and remove or edit these links so that they point to an available page with content.
- 500 = Internal server error. As the name suggests, this is an internal error. It is therefore necessary to check where the problem has occurred.
- 503 = Service Unavailable. It’s a good idea to check the page manually, as it’s probably not allowing bots to crawl the content.
How to find broken links on your website in bulk
To help you learn how to quickly find broken links or redirects on your website, we have created this short video tutorial. Or read the step-by-step guide below.
How to check your HTTP status code in bulk
Start by clicking the Create report button and selecting the country you want data for and the Status code checker.
After selecting the tool, you will see a window with settings to set up the user agent to crawl your data. This is what Marketing Miner will act like when it crawls your list of URLs. It can be seen as MarketingMiner bot, Googlebot, or others.
In general, we recommend choosing the default option – MarketingMiner bot. However, sometimes it is necessary to check if e.g. Google can also crawl your content.
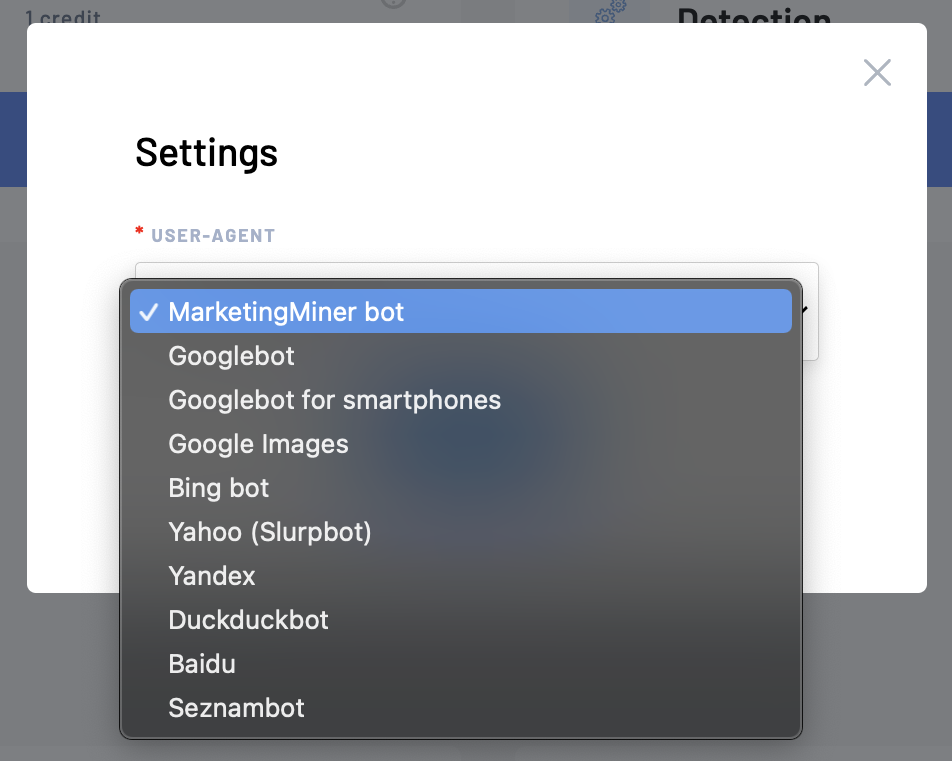
Then click on Next Step to continue. Name your report and add a list of URLs you want to check. You can either enter the list manually, upload a file or sitemap, or import your data from Google Analytics, Google Search Console, or Google Sheets.
You will usually use this tool to analyze the status codes for all the URLs stored in your sitemap. For this instance, select Import Data from URL and enter your sitemap URL to upload it.
Then, click on Import Data to create your Status Code report.
Once the report is generated, you will be emailed the analyzed data.
Status Code report example
Report columns
- Input: Crawled URL by Status Code checker.
- First Status Code: The first status code of the URL. See above for what they mean.
- Last Status Code: The last status code returned from the link.
- Status Code chain: The sequence of status codes returned.
- Last available URL: If the last status code returned is 40x or 50x, web.archive.org will be displayed in this column to show what the pages looked like in the past (if data is available).
Report data
- When analyzing the status codes, focus on the internal server errors (status code 500), identify the problem, and fix it.
- Then check the pages with 404 and 410 status codes. If possible, redirect these URLs to the appropriate pages and remove the internal links pointing to these error pages.
- Check for redirects with status code 302 and verify that this is actually a temporary redirect. If not, use the 301 status code instead.
