Site indexing is one of the most important elements of SEO, as search engines will not be able to display your content in the search results if your site has not been indexed. So, if you want to improve your visibility in search engines, the first thing you need to do is ensure that your web pages are indexed. If they are not, you need to find out why. If the reason is obvious, that’s good, and you don’t need to worry about anything else.
But if you’ve noticed that something is wrong and you don’t know what it is, you need to find it. Marketing Miner will help you to do that, no matter if you need to analyze one URL or a thousand of them.
How can Indexability Checker help your SEO efforts?
This is where the Indexability Checker can be of help:
- If you just got a new project and you need to take care of initial SEO audit. One of the most important steps is to find out if the pages are indexable.
- If you have noticed a drop in your ranking or lower / no traffic from an organic search to a specific page.
- If you are in the process of updating or creating a new sitemap and you only need to include URLs that are indexable.
- When checking if your sitemap contains only indexable URLs.
How to use Indexability Checker
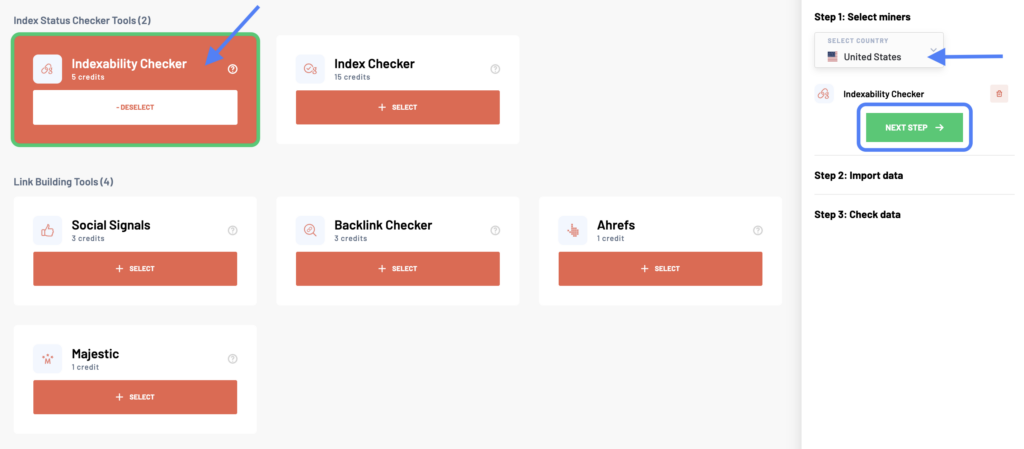
After logging into your Marketing Miner account, click the Create Report button at the top right corner. Then, select the Indexability Checker and target country.
In the next step, enter a list of all the web pages you want to analyze. There are more ways how to do it. You can either copy-paste different URLs (one per row), upload a data file, add a sitemap, or import data from external tools (Google Analytics, Search Console, or Google Sheets).
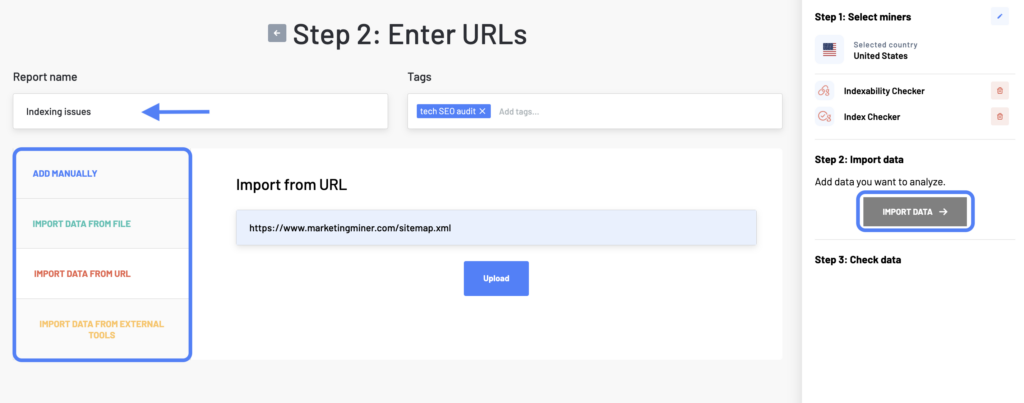
Then click on the Import Data button to check your data before analyzing. If you work with a large number of URLs, we will notify you via email when your report is ready.
Indexability Checker report example
Report columns
- Indexability status: Summary of whether the page is indexable. If not, you’ll find the reason in this column.
- Robots.txt: Indicates whether the URL is blocked in robots.txt or not.
- Link Canonical: Canonical in the source code (if available).
- Canonical Header: Canonical in the header (if any).
- X-robots-tag: If an x-robots-tag is sent in the header, it can block the robot from browsing the page. If the column is empty, then everything is in order.
- Meta robots: The meta tag robots you have on the page. If you don’t have them on the page, there will be a description “missing” in the column value.
- rel = “next”: Content rel = “next” in pagination.
- rel = “prev”: Content rel = “prev” in pagination.
Report data
Now that your report is created, what do you do next? Well, let’s look at a few of the things you need to make sure you don’t overlook:
- First, have a look at the indexability status column and see if your page is indexable. If not, find out why. If you are aware of this situation, it’s all fine. However, it is often the case that you are not aware of it and that someone has unknowingly made the URL non-indexable. Unfortunately, this often happens in web dev departments.
- You can also check your robots.txt to see if the page is blocked for search engines or not. Or you can check the meta robots column, where there are tags like index, noindex, follow, nofollow. Noindex means that the page is not indexable. If this is an accidental situation, change the noindex attribute to index or delete the URL from robots.txt.
- Unless you have a large or very complicated site, we don’t recommend experimenting with index and noindex. Try to make every URL indexable, unless you have a very good reason to do the opposite.
- If you have URLs on the web that you don’t want to index, and Marketing Miner has found these URLs in your sitemap, it’s a good idea to clean up your sitemap. It should not contain any URLs that you don’t want to have in the search index.
