Site indexing is one of the most crucial SEO elements as search engines can’t show your content in search results if your site is not indexed. So, if you want to improve your search visibility, you must first ensure your web pages are indexed.
Indexing issues can occur on any website and can have a disastrous effect on its organic search performance. Sometimes, it just happens that search engines don’t index some content or pages on your site. To quickly find out which URLs are not indexed, use Index Checker, which also discovers the reason why.
Search engines do not allow bulk indexing. Even tools such as Google Search Console don’t provide all the information for indexed page and the Indexing Report has its limitations. The “site:” command is not 100% accurate and can be very misleading too.
So how can you check in bulk whether your pages are indexed and if there are any issues? Try our bulk Index Checker to find out!
When to use Bulk Index Checker?
You can use the Bulk Index Checker:
- If you have started working on a new website or doing a technical SEO audit. You have to find out if your URLs are correctly indexed first so they can drive traffic to the site.
- Have you recently noticed a drop in your organic traffic? This tool will help you quickly determine which URLs and web pages have been removed from the Google Index.
- In Marketing Miner, you can analyze up to 100,000 URLs per report. So you can check the indexing status of large websites and identify which pages are indexed correctly and which aren’t.
Let’s start from the very beginning.
What is indexing in SEO?
Search engines crawl billions of different web pages every day. They crawl content via links so it can be stored and organized in an extensive database for quick retrieval. The search engine’s database is called an index. Indexing is the process of storing web pages in the index. However, not all links are important to these crawlers and may not be indexed by search engines. Content that is not in the index has no chance to rank at all.
Indexing helps search engines organize content during the crawling process, so users receive super-fast responses to their queries.
Can pages be removed from the index?
The short answer is: yes. Any page (that has been already indexed) can be suddenly removed from the search engine’s index. There are more reasons for this:
- This page suddenly stopped working and either returned a 4xx or 5xx error code to tell search engines that the old link should be removed from their crawl index.
- The page is blocked by a robots.txt file that tells search engines not to crawl it.
- A search engine has taken manual actions on your site and removed it entirely from search results. It could be because of its outdated or inappropriate content.
If you want to see whether search engines have indexed your web pages, we recommend you use the Indexability Checker, which explores in more detail why the page has not been indexed.
Checking if your page is indexed by search engines
There are a few useful tools to check the indexing status of your web pages. You can simply use different search engines and their tools. Here is how to do it:
Google index check
Previously, the info: search operator on Google gave users information about websites and additional links to the site too. It was the fastest way to check whether a specific page had been indexed. However, the whole section of such search results was removed back in March 2019 and Google no longer supports this search operator. For this reason, Google search operators are not the fastest and 100% accurate way of checking your indexed pages.
Checking indexed pages in Google Search Console
You can use the URL inspection tool that provides index information about your web pages directly from the Google index. If the page is indexed, you can also check information and status about any addition enhancements Google found on the page.
To see the page’s current index status, enter the URL into the search bar. It’s important to note that before using Search Console, you must also verify your site ownership first. After that, you will be able to see detailed information about your indexing issues:
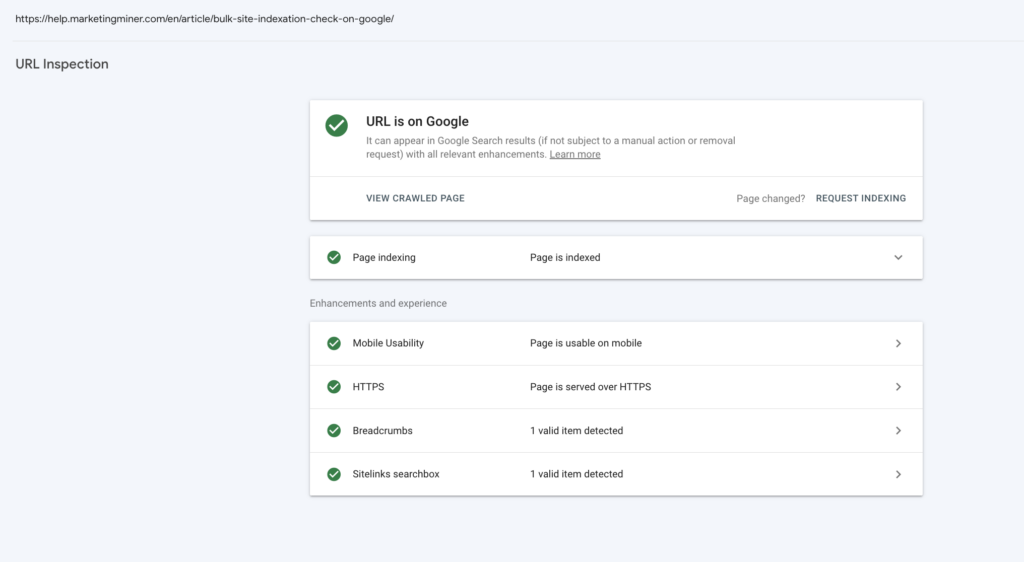
If your newly published page has been discovered but not indexed, there is no need to panic. It usually takes a few days for Google to index the page, or you can also request manual indexing directly in Search Console.
Another way to check indexing issues is the Index Coverage report in Search Console. You can find it by clicking Pages under Index in the left navigation menu. At the top of the page, you will see a graph and count of your indexed and non-indexed pages.
The Why pages aren’t indexed table below highlights issues that prevent different URLs from indexing your content. You can also request to validate the fix directly in this section. But remember, these URLs are only examples, as Search Console doesn’t list all your affected pages.
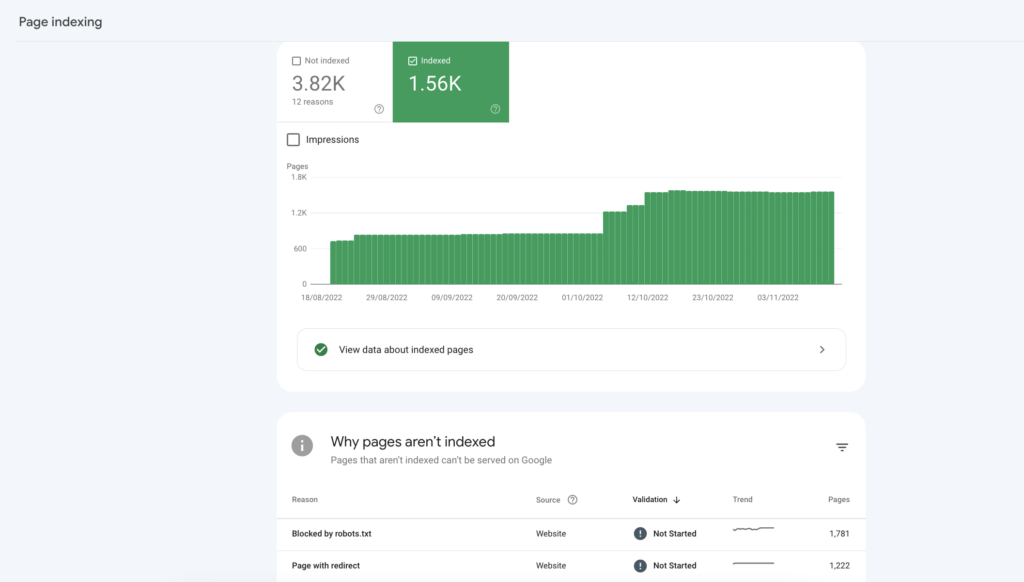
Google Search Console has a daily limit of inspection requests for each website you have access to, and it does not necessarily show all affected URLs. The list is limited to 1,000 rows. So what if you want to check thousands of pages to see if they are all indexed? This is when you can use Marketing Miner’s Index Checker.
How to check your indexing status in bulk
After logging into your Marketing Miner account, click the Create Report button at the top right corner. In the Reports section, start by selecting your country and the Index Checker tool to check your page’s indexing status.
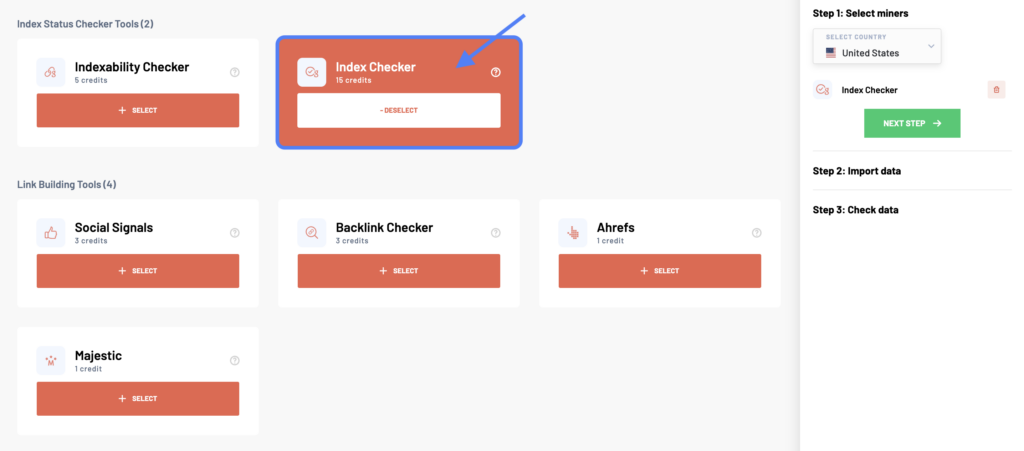
In the next step, enter a list of all the web pages you want to analyze. There are more ways how to do it. You can either copy-paste different URLs (one per line), upload a data file, add a sitemap, or import data from external tools.
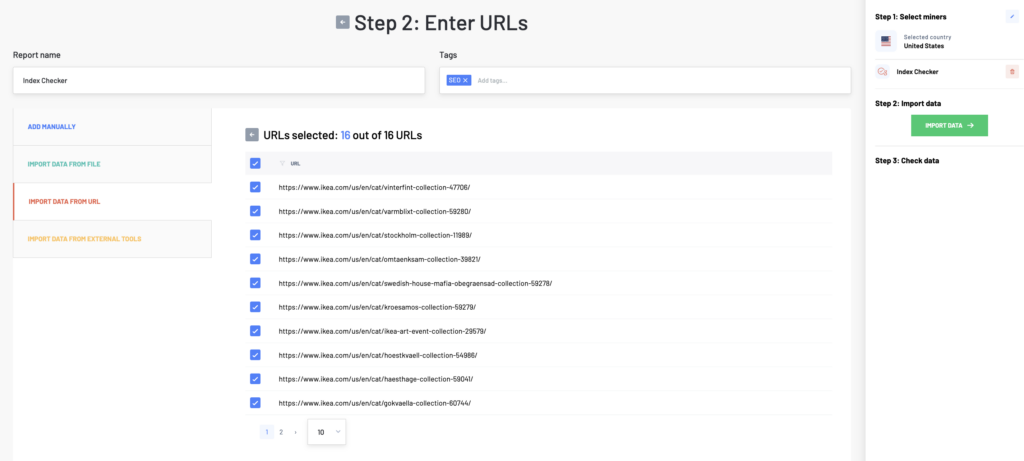
Then click on the Import Data button to check your data before analyzing. If you work with a large number of URLs, we will notify you via email when your report is ready.
Index Checker example report
Index Checker – data colums
- Input: URLs of web pages you want to check
- Indexed by Google: Detecting whether the URL is indexed by the search engine or not. It returns either yes (indexed) or canonicalized or not indexed (as Google doesn’t support the info search operator anymore, so we can’t assess whether the URL is not indexed or just canonicalized to another URL).
Index Checker Report – what to do next?
Identify non-indexed pages – You should primarily focus on the Indexed by Google column with the indexing status of different URLs. You can also apply a filter to only see non-indexed pages. Then, you can use this list in the next step to explore why they aren’t shown in the search engine results and how to fix them. Next, you can use the Indexability Checker to help you discover the issues.
